permanent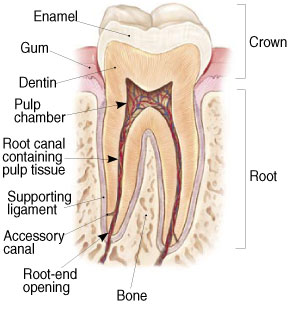 “Endo” is the Greek word for “inside” and “odont” is Greek for “tooth.” Endodontic treatment treats the inside of the tooth.
“Endo” is the Greek word for “inside” and “odont” is Greek for “tooth.” Endodontic treatment treats the inside of the tooth.
To understand endodontic treatment, it helps to know something about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is a soft tissue called the pulp. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue and creates the surrounding hard tissues of the tooth during development.
The pulp extends from the crown of the tooth to the tip of the roots where it connects to the tissues surrounding the root. The pulp is important during a tooth’s growth and development. However, once a tooth is fully mature it can survive without the pulp, because the tooth continues to be nourished by the tissues surrounding it.
If this pulp tissue becomes infected or inflamed, it often will become painful or swollen. Even if pain is not present, this disease of the pulp will eventually lead to loss of the tooth. Root canal therapy removes this diseased tissue and cleanses the spaces in the tooth and root so the body can heal itself. Once the space is cleansed, it must be sealed to help prevent reinfection. Finally, the tooth is restored in form so it may remain strong and functional.
What is Traditional Endodontic treatment?
Procedure Summary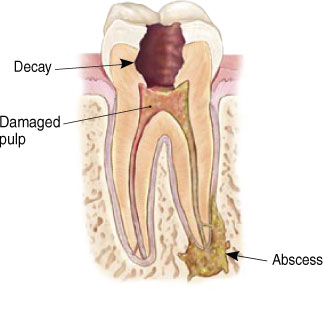
1. The endodontist examines and x-rays the tooth, then administers local anesthetic. After the tooth is numb, the endodontist places a small protective sheet called a “dental or rubber dam” over the area to isolate the tooth and keep it clean and free of saliva during the procedure.
2. The endodontist makes an opening in the crown of the tooth. Very small instruments are used to clean the pulp from the pulp chamber and root canals and to shape the space for filling.
3. After the space is cleaned and shaped, the endodontist fills the root canals with a biocompatible material, usually a rubber-like material called “gutta-percha.” The gutta-percha is placed with an adhesive cement to ensure sealing of the root canals. In most cases, a permanent filling is placed to close the opening. Sometimes a temporary filling is places. This temporary filling will be removed by your dentist before the tooth is restored.
4. After the final visit with your endodontist, you must return to your dentist to have a crown or other restoration placed on the tooth to protect and restore it to full function. If the tooth lacks sufficient structure or could use help to hold the restoration in place, the endodontist may place a post inside the tooth. Ask your dentist or endodontist for more details about the specific restoration planned for your tooth.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Why would I need an Endodontic procedure?
Endodontic treatment is necessary when the pulp, the soft tissue inside the root canal, becomes inflamed or infected. The inflammation or infection can have a variety of causes: deep decay, repeated dental procedures on the tooth, or a crack or chip in the tooth. In addition, an injury to a tooth may cause pulp damage even if the tooth has no visible chips or cracks. If pulp inflammation or infection is left untreated, it can cause pain or lead to an abscess.
What are the signs of needing Endodontic treatment?
Signs to look for include pain, prolonged sensitivity to heat or cold, tenderness to touch and chewing, discoloration of the tooth, and swelling, drainage and tenderness in the lymph nodes as well as nearby bone and gingival tissues. Sometimes, however, there are no symptoms.
How does Endodontic treatment save the tooth?
The endodontist removes the inflamed or infected pulp, carefully cleans and shapes the inside of the canal, a channel inside the root, then fills and seals the space. Afterwards, you will return to your dentist, who will place a crown or other restoration on the tooth to protect and restore it to full function. After restoration, the tooth continues to function like any other tooth.
Will I feel pain during or after the procedure?
Many endodontic procedures are performed to relieve the pain of toothaches caused by pulp inflammation or infection. With modern techniques and anesthetics, most patients report that they are comfortable during the procedure.
For the first few days after treatment, your tooth may feel sensitive, especially if there was pain or infection before the procedure. This discomfort can be relieved with over-the-counter or prescription medications. Follow your endodontist’s instructions carefully.
Your tooth may continue to feel slightly different from your other teeth for some time after your endodontic treatment is completed. However, if you have severe pain or pressure or pain that lasts more than a few days, call your endodontist.





